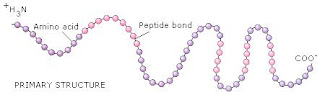
First Level- Primary Structure
A linear sequence of the amino acids joined by peptide bonds (think of the structure like a necklace and the amino acids are the different beads).
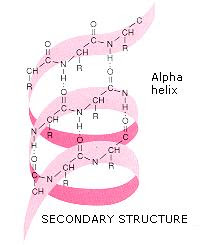
Second Level- Secondary Structure
The second structure comes about when the polypeptide takes on a certain orientation in space, the structure is an alpha helix. Hydrogen bonding between peptide bongs holds the shape in place.

Third Level- Tertiary Structure
The structure is now finally a three-dimensional shape in this structure. The helix folds into a
characteristic globular shape due in part to covalent bonding between 'R' groups. ('R' groups are alanine, valine, cysteine, and phenylalnine.) The shape is maintained by various types of bonding; covalent, ionic, and hydrogen.
Fourth Level- Quaternary Structure
This level occurs when two or more polypeptides join to form a single protein.
Proteins, which have levels of organization, are important in the structure and the function of cells. Some proteins are enzymes, which speed chemical reactions.
Abby
Kristen
Cooper
Erik
How do changes in the tertiary structure of a protein influence its functionality in biological systems?
ReplyDeleteMight wanna change "bongs" to bonds
ReplyDelete